Google Cache Checker Tool – Free SEO Guide
Google Cache Checker Tool – The Ultimate Guide for SEOs & Webmasters

Introduction
Have you ever made changes to your website, only to wonder whether Google has actually noticed them yet? You update titles, rewrite blog posts, or redesign a page — but in search results, Google might still be showing the old version. The secret lies in something many website owners overlook: Google Cache.
Google Cache is essentially a snapshot of your webpage stored on Google’s servers. It represents how Googlebot saw your site during its last crawl. For webmasters, SEOs, and digital marketers, this cached version can reveal a lot: whether Google has indexed your updates, whether your site is properly crawlable, or even if there’s an underlying problem like a hack or cloaking issue.
That’s where a Google Cache Checker Tool becomes invaluable. Instead of manually digging through Google search operators, a cache checker instantly shows you the cached version of any page, including the exact date and time it was saved.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll go far beyond the basics. You’ll learn what Google Cache is, why it matters for SEO, how to use a cache checker effectively, common issues to troubleshoot, real-world case studies, expert insights, and best practices for making cache analysis part of your regular SEO workflow.
👉 Quick Access: Want to see how Google currently views your site? Try our Google Cache Checker Tool right now.
Section 1 – Foundations
What is Google Cache?
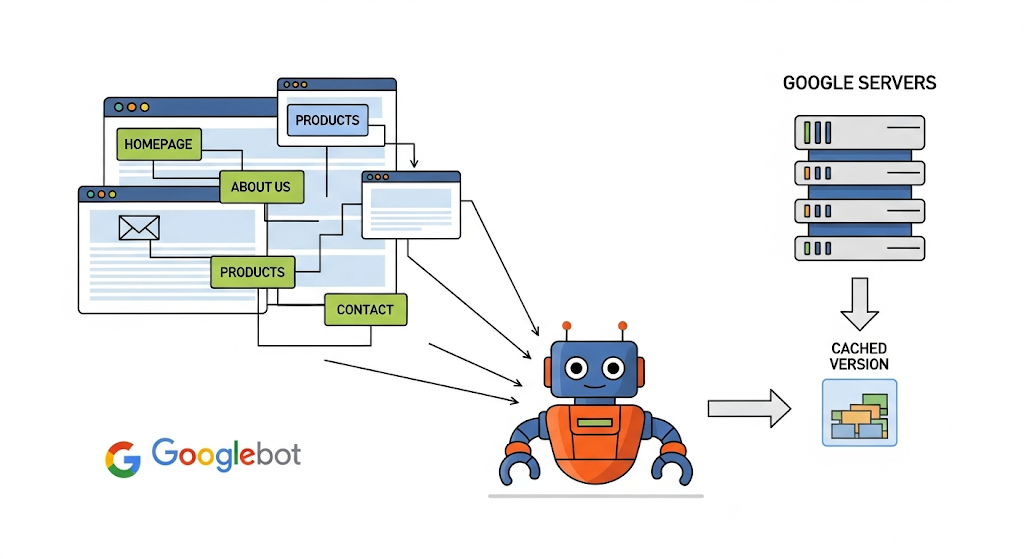
Google Cache is a stored copy of a webpage that Googlebot saves when crawling your site. Think of it as a “freeze-frame” of your content. The cache isn’t updated in real time — it reflects what Googlebot saw during its last successful crawl.
When you search for a website in Google and click the small arrow or menu next to a result, you might see the option “Cached.” That page shows Google’s stored version, not the current live version.
In simple terms:
The live page is what visitors see in real time.
The cached page is what Google last stored.
Google maintains these snapshots for faster page retrieval, troubleshooting, and, in some cases, user accessibility (for example, if the live site is temporarily down).
Why Does Google Cache Matter for SEO?
For SEOs and webmasters, Google Cache is more than a curiosity — it’s a diagnostic tool. The cached version helps answer critical questions:
Is my page being indexed properly?
If your latest content isn’t reflected in the cached version, it may not be indexed yet.
How fresh is my content to Google?
By comparing cache dates, you can see how often Google crawls your site.
Has my site been hacked or cloaked?
Sometimes attackers show one version to users and another to Googlebot. A cache check reveals the hidden version.
Why aren’t my changes showing up in search results?
If the cache is outdated, it explains why titles, descriptions, or new content aren’t yet visible.
Example: A travel blog once discovered that despite updating articles daily, Google’s cached copy was two weeks old. The issue wasn’t with indexing but with crawl frequency, which the webmaster resolved by improving internal linking and submitting updated sitemaps.
Section 2 – The Tool in Action
What is a Google Cache Checker Tool?
A Google Cache Checker Tool is a utility that lets you instantly see the cached version of any page. Instead of relying on manual “cache:” search operators, the tool queries Google’s cache database directly and returns the snapshot.
The main advantage is speed and convenience: you don’t need to guess whether Google has refreshed your page — you can confirm it with one click.
Step-by-Step: How to Use a Google Cache Checker Tool
Using the tool is straightforward. Here’s the typical process:
Enter the full URL of the page you want to check.
Click Check or Submit.
The tool sends a query to Google’s cache.
You’ll see the cached version of your page, including the timestamp when it was last saved.
For SEOs, that timestamp is crucial. If you updated your content yesterday but the cache shows a date from three weeks ago, you know Google hasn’t crawled your update yet.
Google Cache Checker Tool – Free Demo
👉 You can try it right now: Google Cache Checker Tool.
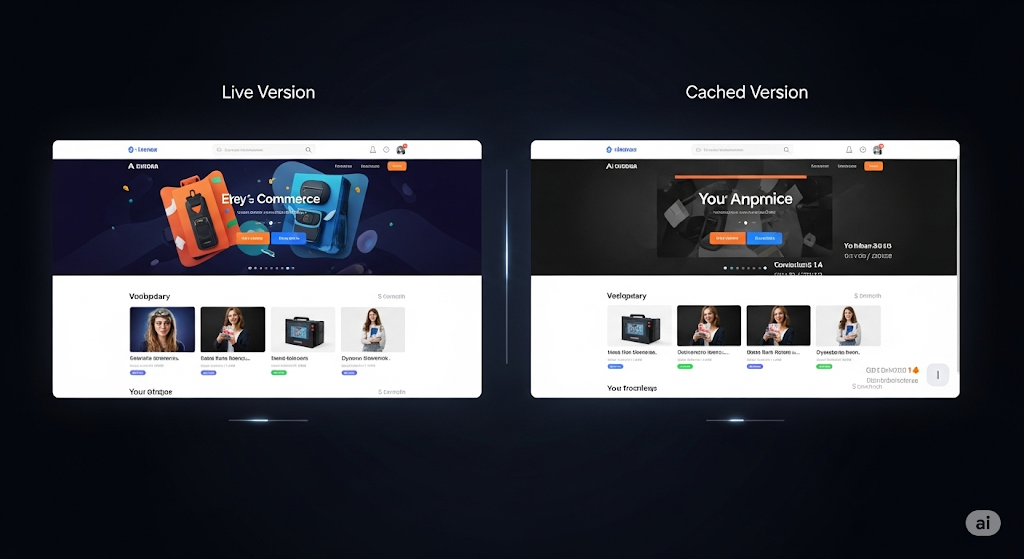
For example, imagine you updated your homepage banner to announce a summer sale. On the live site, the banner says “Summer Deals – Save 30%”. But the cached version still shows “Spring Specials – Save 20%”.
This tells you two things:
Google hasn’t recrawled since the update.
Search results may still display old content, potentially costing you clicks.
Section 3 – Deep Dive Use Cases
Practical Uses of Google Cache for Webmasters & SEOs
Indexation Verification: Confirm whether Googlebot has crawled your latest pages.
SEO Troubleshooting: Diagnose why changes aren’t reflected in SERPs.
Competitor Tracking: See when Google last crawled a competitor’s page.
Content Recovery: Retrieve content from cached versions if the live site is corrupted.
Security Checks: Detect cloaking or injected spam links visible only to crawlers.
How Often Does Google Update Cache?
Google doesn’t update cache on a fixed schedule. Instead, it depends on factors like:
Site authority: High-authority sites get crawled more often.
Content updates: Fresh content triggers more frequent crawls.
Crawl budget: Larger sites with many pages are crawled strategically.
A major news site may get recrawled within hours, while a small local blog might wait weeks. On average, most sites see updates within 7–21 days.
Google Cache vs Wayback Machine: Key Differences
Many confuse Google Cache with the Wayback Machine. Here’s the distinction:
| Feature | Google Cache | Wayback Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Last crawl snapshot | Historical archive |
| Frequency | Days–weeks | Months–years |
| Data Source | Googlebot | Archive.org |
| Best Use Case | SEO diagnostics | Research & digital history |
| Accessibility | Auto-generated | On-demand + automated crawls |
Key Insight: Google Cache is best for short-term SEO monitoring, while the Wayback Machine is useful for long-term archival research.
Common Issues With Google Cache (and Fixes)
No Cache Found: Likely the page hasn’t been crawled yet or is blocked by robots.txt.
Outdated Cache: Google hasn’t recrawled recently. Solution: request indexing in Search Console.
Blank or Error Cache: Check for meta noarchive tags, canonical conflicts, or server errors.
Quick Fix Tip: Use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to request immediate reindexing.
Section 4 – Advanced Insights
Technical SEO & Google Cache
Google Cache often interacts with other technical SEO elements:
Cache-Control Headers: These relate to browser/HTTP caching and don’t directly affect Google Cache, but misconfiguration can confuse crawlers.
Canonical Tags: Incorrect canonicals may cause Google to cache the wrong version.
Meta “noarchive” Tag: Explicitly prevents Google from storing or displaying a cached page.
Mobile vs Desktop Cache: Why They Differ
Since Google’s move to mobile-first indexing, cached pages often display differently between devices. You may see:
A simplified mobile layout in the cache.
Missing elements that appear on desktop.
For diagnosis, always check both mobile and desktop versions to ensure consistent rendering.
Case Studies: Google Cache in Action
Ecommerce Migration: An online store noticed that even after migrating to a new CMS, cached versions still displayed old category URLs. This helped the SEO team identify redirect issues.
Content Updates: A blogger optimized articles with new keywords but rankings didn’t improve. Cache revealed Google hadn’t crawled updates, prompting a reindex request.
Penalty Diagnosis: A business hit by a manual penalty discovered hidden text in the cached page, injected by hackers. The cache helped uncover and remove the malicious code.
Section 5 – Tools & Alternatives
Best Free Google Cache Checker Tools (2025 Edition)
There are several cache tools available, but not all are equally useful. Some popular options include:
SmallSEOTools Cache Checker.
SERanking’s free tool.
SiteChecker.pro Cache Viewer.
CachedView (multi-source cache viewer).
SEO Magnate Cache Checker — the most streamlined and accurate for quick checks.
Alternatives to Google Cache
Wayback Machine: A historical archive of web pages over time.
Bing Cache: Similar to Google Cache, but powered by Bing’s crawler.
Archive.today: Manual one-time captures of webpages.
Section 6 – Tutorials & Step Guides
How to View Google Cache Without Any Tool
You don’t always need a third-party tool. Two easy methods are:
Use the cache: operator in Google Search. Example: cache:example.com/page.
From the SERPs, click the small menu arrow next to a result and choose “Cached.”
This is useful for quick checks but doesn’t provide timestamps or batch functionality like dedicated tools.
How to Force Google to Update Your Cache
If your cached page is outdated:
Update your content.
Open Google Search Console.
Use URL Inspection → Request Indexing.
Wait for Googlebot to recrawl.
While you can’t force Google, this process accelerates reindexing.
Troubleshooting: Why Isn’t My Site Cached?
Common reasons include:
Your site is new and hasn’t been crawled yet.
robots.txt is blocking Googlebot.
A “noarchive” directive prevents caching.
Crawl budget is limited on very large sites.
Fixing these issues often involves updating robots.txt, improving site authority, and ensuring pages are linked internally.
Section 7 – Expert Tips & Insights
Expert Quotes on Google Cache & SEO
John Mueller (Google): “Google Cache isn’t meant to be a reliable reflection of your site — it’s just a snapshot during crawling.”
SEO experts often recommend using cache data as a supporting signal, not as your sole measure of indexing success.
Best Practices for Using Cache Data in SEO Audits
Incorporating cache checks into audits provides clarity. Follow this checklist:
Compare live vs cached content regularly.
Record cache timestamps for important pages.
Use cache to verify that Google sees canonical content.
Investigate unexpected cache differences as potential SEO issues.
Section 8 – FAQs
How do I check if Google cached my site?
You can use cache:yourdomain.com/page in Google or a cache checker tool for easier access.
How often does Google update cache?
Usually every 7–21 days, but frequency varies.
Can cached pages affect SEO?
Not directly, but they reveal how Googlebot sees your site, which influences indexing.
Why is my cached page different from my live page?
Because Google hasn’t recrawled recently, or you’re seeing the mobile-first version.
Does Google cache images or PDFs?
No, cache is usually limited to HTML snapshots.
Can I remove cached pages?
Yes, use the Removals Tool in Search Console.
What’s the difference between index and cache?
Index = stored in Google’s search database. Cache = stored snapshot for reference.
Why does Google show old content in cache?
Because the page hasn’t been recrawled yet.
Is Google Cache reliable?
It’s useful for diagnostics, but not a guaranteed real-time reflection.
How do I clear outdated cache quickly?
Request indexing in Google Search Console.
Conclusion
Google Cache is one of the most underrated tools in an SEO’s arsenal. By regularly checking cached versions of your site, you can confirm whether updates are being indexed, troubleshoot technical issues, monitor competitors, and even recover lost content.
Instead of relying on guesswork, use a dedicated tool to streamline the process. 👉 Try our free Google Cache Checker Tool today and instantly see how Google views your site.
